
Published on June 25, 2024
Cleaning, disinfection and depopulation
Biosecurity is a very important factor to guarantee efficient production and excellent animal viability. In this article, we'll understand why cleaning, disinfection and depopulation are an essential step in the hygiene conduct of the livestock building.
IT MUST BE REMEMBERED THAT THE SUCCESS OF A BATCH IS BEGAN AS SOON AS THE PREVIOUS BATCH LEAVED THE BARN
The cleaning and disinfection site must be organised and planned to ensure maximum efficacy.
After the departure of the animals, whether it is floor rearing or not, the principle remains the same:
- Insect control treatment in the hour following the departure of the breeders. In fact, numerous parasites, such as mealworm beetles, will go and hide as soon as the litter cools. So they must be dealt with when the livestock environment is still warm, i.e. just after the departure of the animals. Furthermore, cleaning and disinfection must be suitable for each type of parasite (coccidia, worms, lice, etc.).
- Placement of pest control bait. The time is right because there is no other feed present in the building at this stage.
- Dismantling and removal of rearing equipment (drinkers, feed chains, weighing equipment, etc.) outside the production building on a concrete hardstanding.
- Removal of work clothes not used for cleaning the building.
- Draining of water circuits.
- Removal of droppings and/or litter.
- Washing of walls, floors, ventilation and heating systems, pipework, water containers, silos.
- Maintenance of the interior of the building (pipework and watering systems, ventilation and aeration, feed system)
- Washing of rearing equipment outside the building on a concrete hardstanding fitted with a system for collecting the washing water.
- Inspection and servicing of rearing equipment.
- Entry of clean rearing equipment into the building.
- Washing of the building surrounds, of all the concrete surfaces and the water drainage pipes.
- Control of the building impermeability (control of intrusion by rodents and other pests).
- Washing of work clothing specific to the production building.
- Liquid disinfection of the pipework for water.
- Once the building is dry, disinfection of the building and all the equipment inside (disinfection of the space by thermal fogging or fogging).
- Closure of the building for a minimum of 24 hours then airing, followed by depopulation for at least 21 days (closed building).
- Disinfection of the site surroundings.
- New placement of pest control bait.
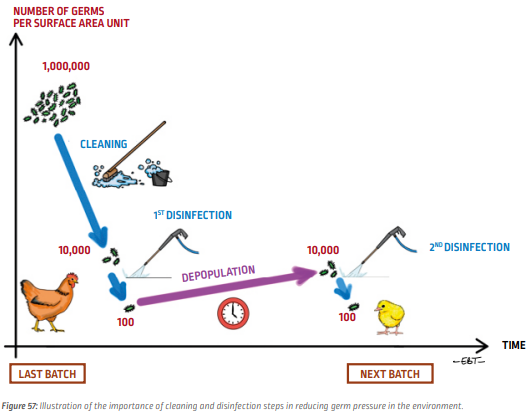
Throughout the entire depopulation period, access to the livestock building is prohibited. The succession of washing, disinfection and depopulation makes it possible to decrease the microbial load in the building.

Technical tip
As everywhere in biosecurity, washing is essential technique because it is the most important operation for decreasing the microbial load. Generally, it should be remembered that disinfection is only satisfactory on a correctly washed surface.




